Website security is becoming increasingly important as digital threats continue to rise. One way to ensure communication security between users and servers is by using an SSL (Secure Socket Layer) Certificate. SSL works by encrypting transmitted data, preventing third parties from accessing it. Currently, two types of SSL certificates are available: free and paid. But what are their differences, and which is more suitable for your needs?
Two Types of SSL Certificates
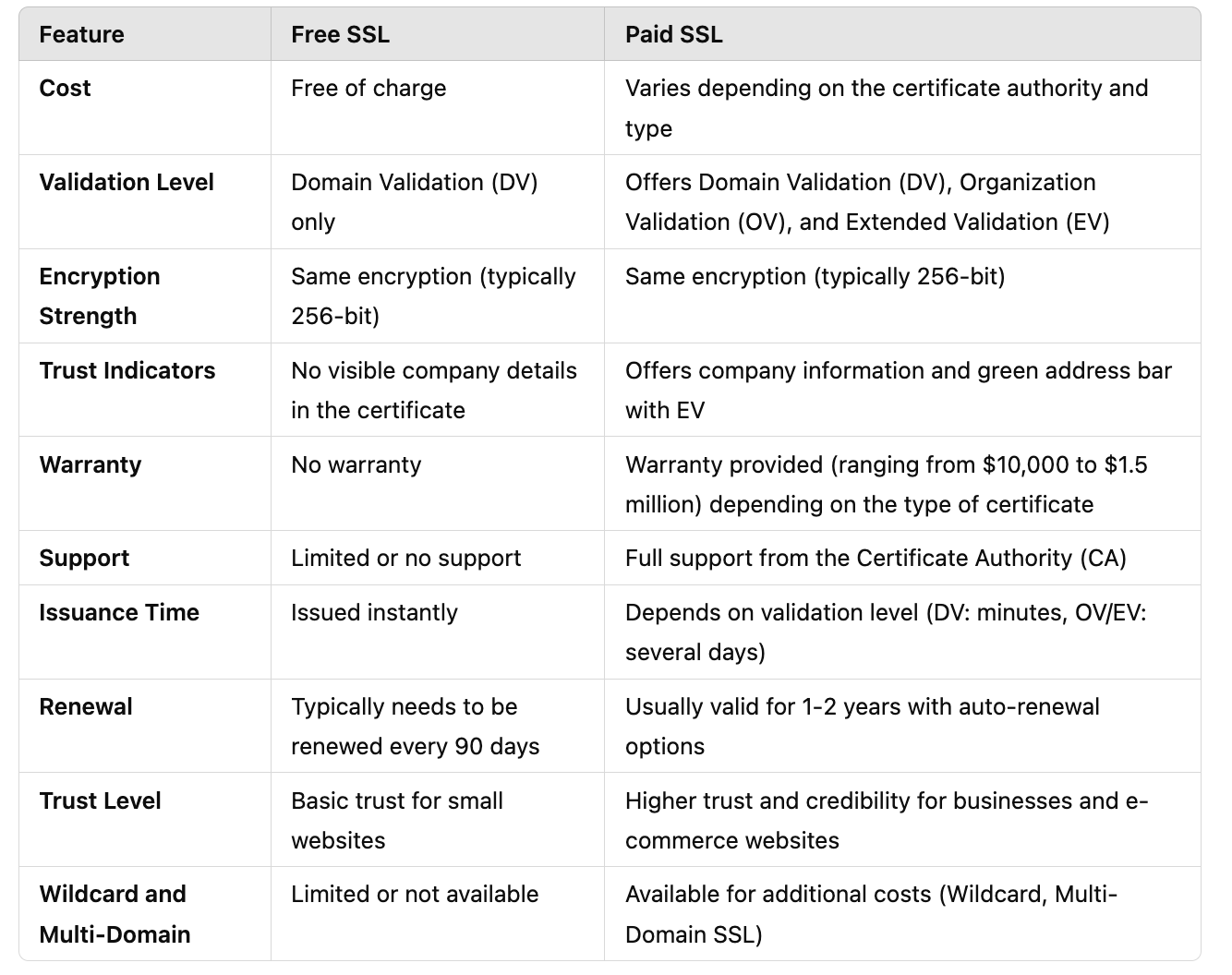
In the digital world, two types of SSL Certificates are available in the market: Free SSL Certificates and Paid SSL Certificates. As the name suggests, Free SSL Certificates can be obtained at no cost, typically through services like Let’s Encrypt. On the other hand, companies or individuals need to pay commercial authorities such as Symantec, Comodo, DigiCert, or Sectigo to get a paid SSL certificate.
Although there are significant differences between Free SSL and Paid SSL, the level of encryption provided by both is the same. Both use the same strong encryption technology to protect the data transmitted between the server and the user. So, the question arises: If the encryption is the same, why pay for an SSL certificate?
The answer lies in several important differences beyond the encryption itself, which affect the level of trust, support, validation, and additional features each type of SSL certificate offers.
1. Validation and Trust
Free SSL usually only supports domain validation (Domain Validation – DV). This means the certificate authority only verifies that you own or manage the domain you registered for SSL without ensuring whether you are a legitimate organization.
On the other hand, Paid SSL offers stronger validation options like Organizational Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV), which provide a higher level of trust to users. EV Certificates, for instance, allow your company name to appear in the browser address bar, adding credibility and trust for site visitors. Additionally, for companies handling a lot of data and transactions, it is recommended to use a paid SSL for security and to increase credibility in the eyes of customers and business partners, which ultimately can boost conversions and customer loyalty.
2. Financial Guarantees and Insurance
Paid SSL often comes with financial guarantees or insurance that provide compensation if a security breach related to the certificate occurs. If you rely on Free SSL, no compensation or guarantees are offered. Therefore, for sites handling financial transactions or sensitive data, using a Paid SSL with insurance is important to protect the business and users.
3. Support Services
If you encounter issues with a Free SSL Certificate, support is usually limited to community forums or online documentation. In contrast, paid SSL typically comes with professional technical support ready to assist if any issues arise. This is crucial for businesses needing quick resolution of security or SSL configuration issues.
4. Validity Period and Renewal
Free SSL Certificates generally have a shorter validity period, often only 90 days, requiring more frequent renewals. Although there is an option for automatic renewal, this process can be cumbersome if done manually. On the other hand, Paid SSL Certificates usually last 1 to 2 years and are easier to renew without requiring frequent manual actions.
Read other articles, such as Introduction to SSL and TLS, Explanation, and Functions.
5. Additional Features
Paid SSL often offers various additional features not found in Free SSL. For example, you can get a Wildcard SSL Certificate, which allows you to secure all subdomains under one domain. There is also Multi-Domain SSL, which allows you to secure multiple domains simultaneously with a single certificate. These features are very beneficial for large companies or businesses managing multiple websites.
6. Security Level to Suit Needs
Although the encryption between Free SSL and Paid SSL is the same, the security difference lies in the more comprehensive validation provided by Paid SSL. For blogs or personal sites that do not process sensitive information, Free SSL is sufficient. However, for e-commerce sites, companies, or platforms handling financial information and personal data, Paid SSL offers an additional layer of protection and stronger trust for users.
Difference Table Between Free and Paid SSL
Here is a description for the difference table between Free and Paid SSL:
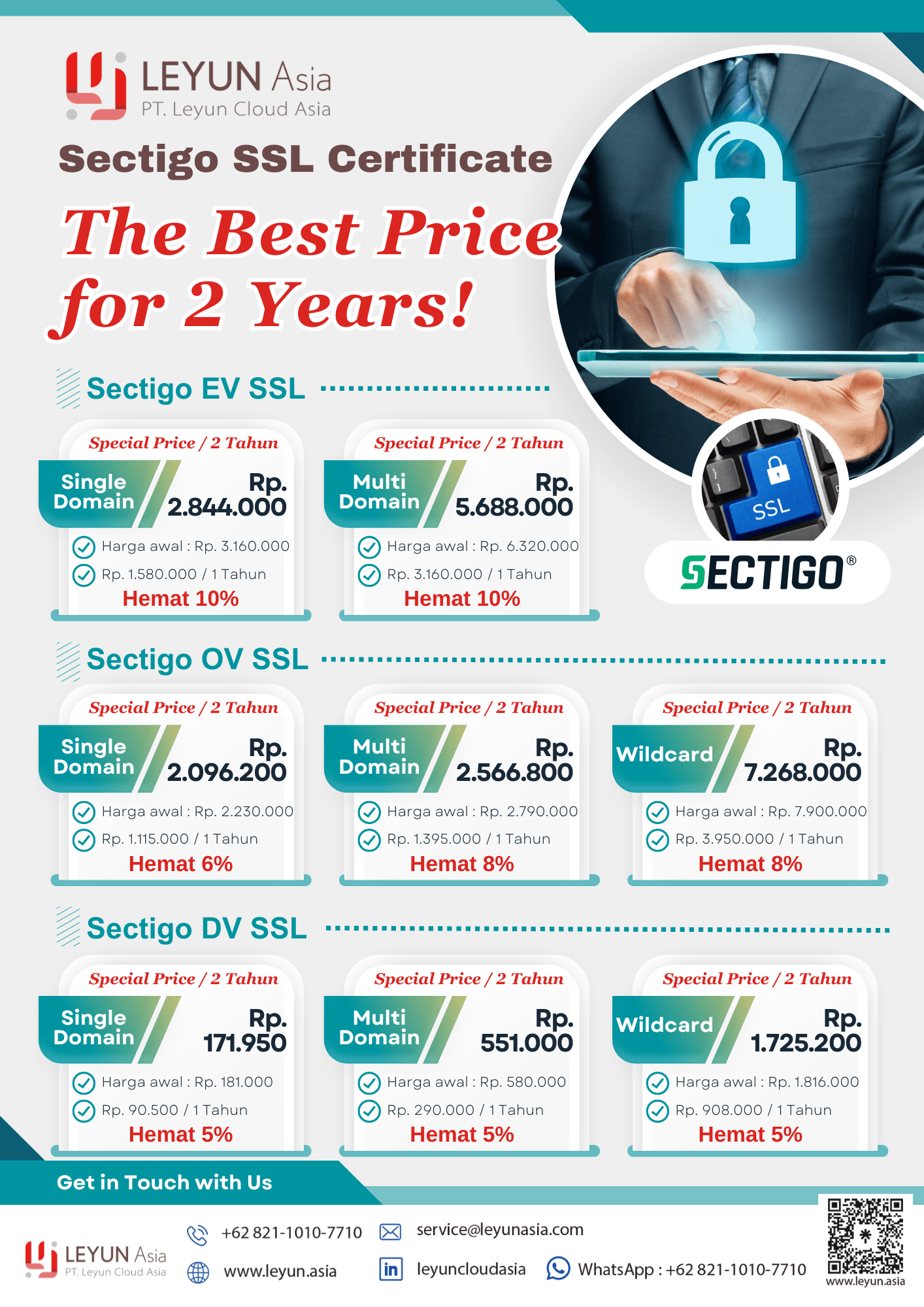
SSL Sectigo Promo from Leyun Cloud Asia
Get the special promo this month, consult with our team immediately by filling out the form below: